
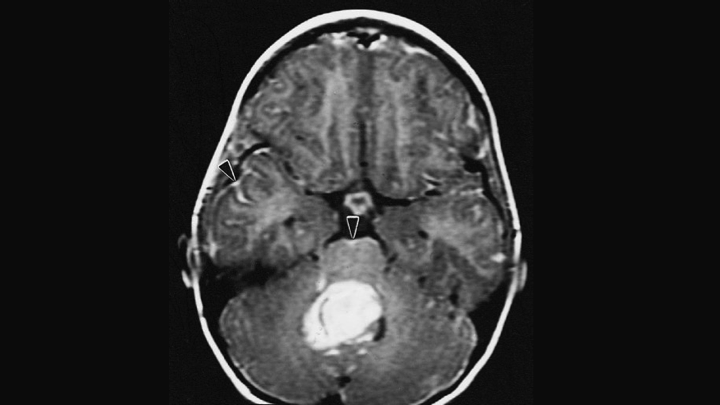
In sum 24 treatment plans for 6 pediatric patients were realized. Treatment of adults with medulloblastoma is largely based on data regarding the treatment of children.This study aimed to contrast four different irradiation methods for pediatric medulloblastoma tumors in a dosimetric comparison regarding planning target volume (PTV) coverage and sparing of organs at risk (OARs). Concurrent chemotherapy is sometimes used as well, but this remains controversial with the biggest concern of depressed blood counts given the amount of bone marrow irradiated.Ĭraniospinal irradiation remains the cornerstone of therapy followed by adjuvant chemotherapy. Overall, given the large volume irradiated, more advanced techniques such as proton therapy, tomotherapy, or IMRT have been utilized to decrease acute and late effects of treatment. Given this, specific contouring guidelines are important to include the cribriform plate and other foramina that contain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) with more targeted plans. In the 3D conformal era for craniospinal irradiation, these areas were automatically included in the fields. This chapter describes specific directions for inclusion of all areas of CSF and planning pearls. KeywordsĪjithkumar T et al (2018) SIOPE-brain tumor group consensus guideline on craniospinal target volume delineation for high-precision radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 128(2):192–197Ĭao F, Ramaseshan R, Corns R, Harrop S, Nuraney N, Steiner P, Aldridge S, Liu M, Carolan H, Agranovich A, Karvat A (2012) A three-isocenter jagged-junction IMRT approach for craniospinal irradiation without beam edge matching for field junctions. Lin H, Ding X, Kirk M, Liu H, Zhai H, Hill-Kayser CE, Lustig RA, Tochner Z, Both S, McDonough J (2014) Supine craniospinal irradiation using a proton pencil beam scanning technique without match line changes for field junctions.
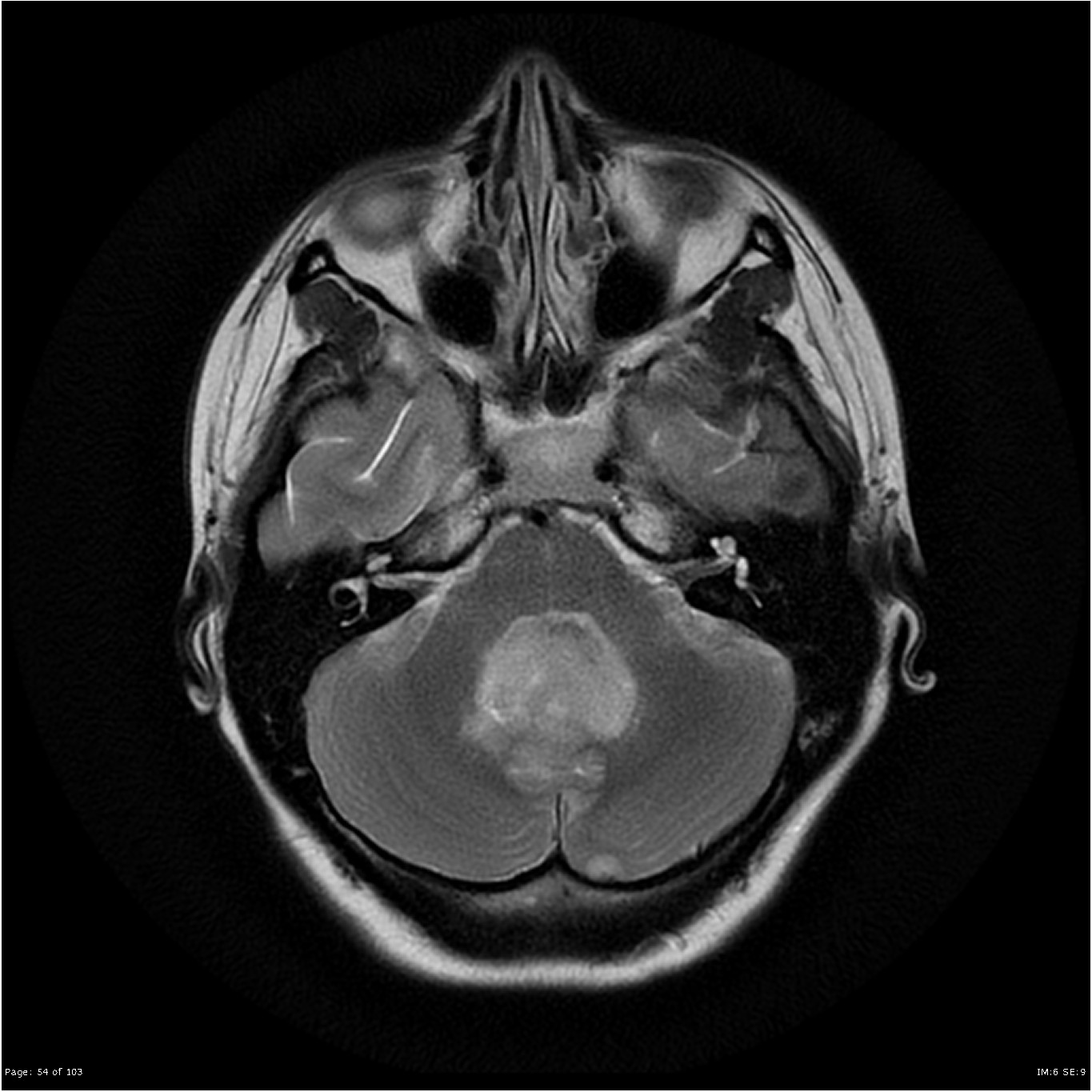
Paulino AC, Lobo M, Teh BS, Okcu MF, South M, Butler EB, Su J, Chintagumpala M (2010) Ototoxicity after intensity-modulated radiation therapy and cisplatin-based chemotherapy in children with medulloblastoma. Haas-Kogan D et al (2013) National Cancer Institute Workshop on proton therapy for children: considerations regarding brainstem injury. IJROBP 101(1):153–168īrown AP et al (2013) Proton beam craniospinal irradiation reduces acute toxicity for adults with medulloblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 86(2):277–284įranceschi E, Hofer S, Brandes AA et al (2019) EANO-EURACAN clinical practice guideline for diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of post-pubertal and adult patients with medulloblastoma.
#Qarc medulloblastoma trial
Merchant TE et al (2008) Multi-institution prospective trial of reduced-dose craniospinal irradiation (23.4 Gy) followed by conformal posterior fossa (36 Gy) and primary site irradiation (55.8 Gy) and dose-intensive chemotherapy for average-risk medulloblastoma. Michalski JM et al (2016) Results of COG ACNS0331: a phase III trial of involved-field radiotherapy (IFRT) and low dose craniospinal irradiation (LD-CSI) with chemotherapy in average-risk medulloblastoma: a report from the Children’s Oncology Group.Bernadine Donahue 1*, Mary A.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
